Hans Selye Defined His General Adaptation Syndrome Concept, Which Is Also Known As:
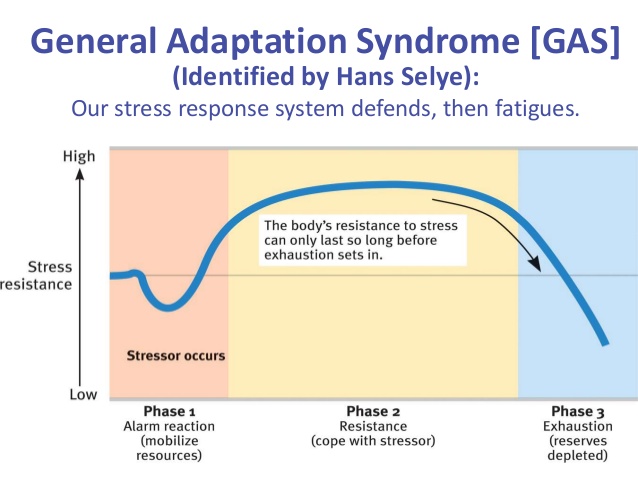
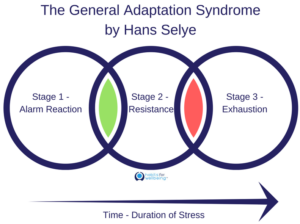
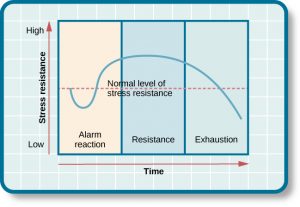
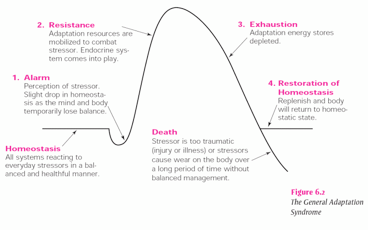
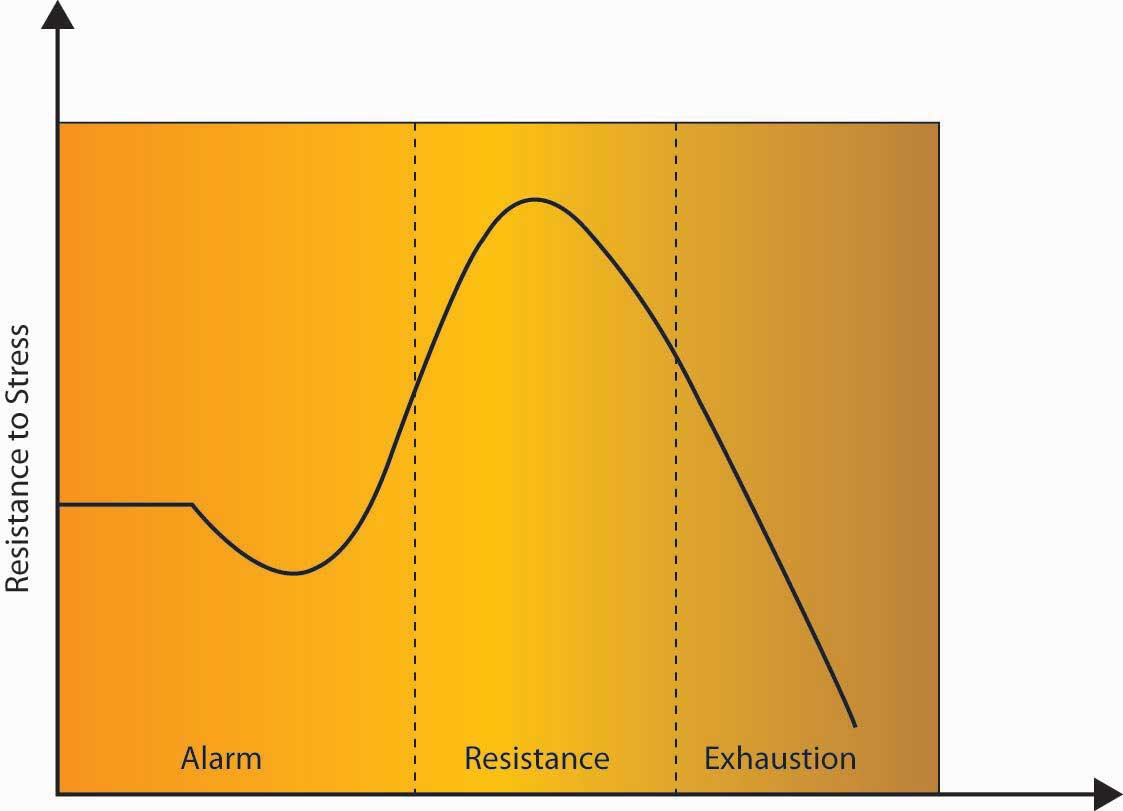
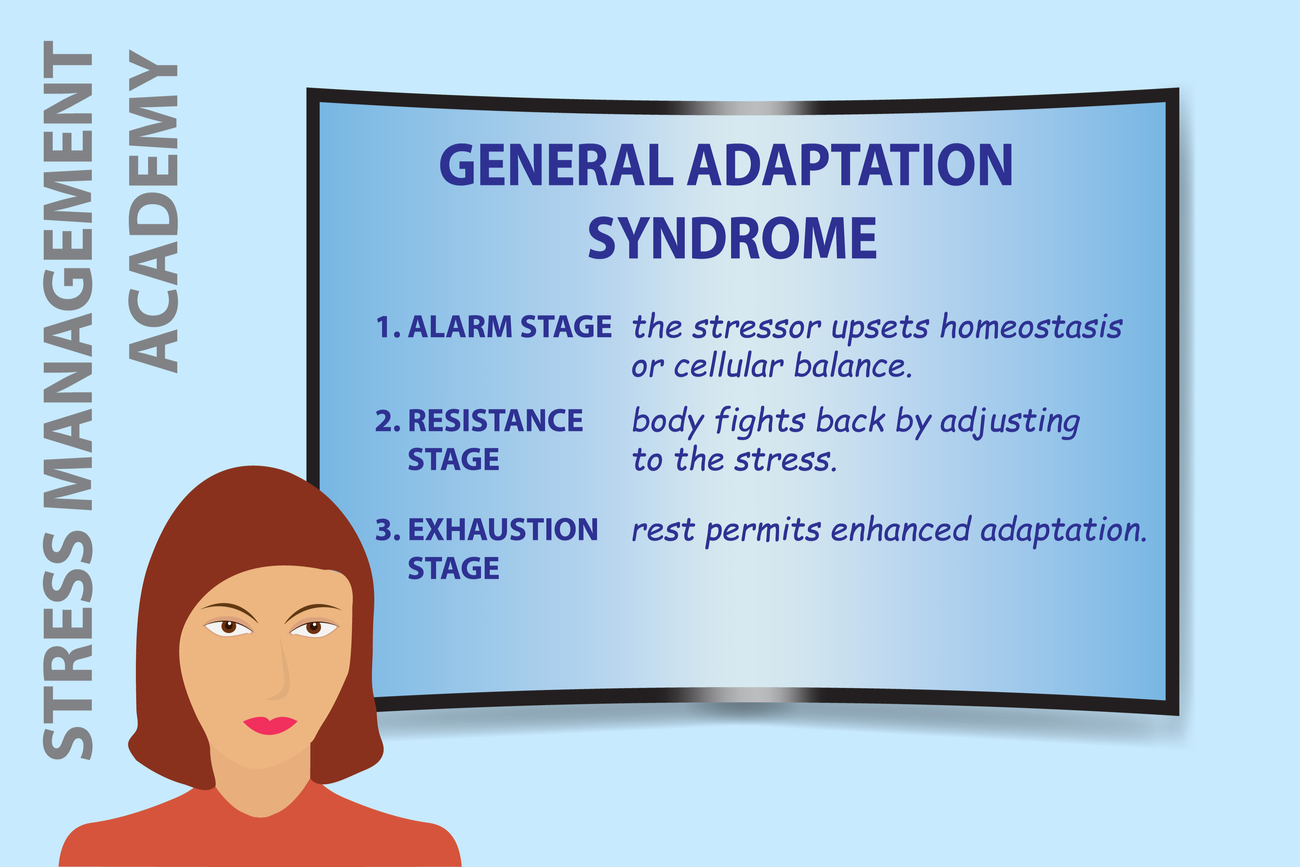
Hans selye defined his general adaptation syndrome concept, which is also known as:. General adaptation syndrome is a three-stage response that the body has to stress. The alarm stage the resistance stage and the exhaustion stage Evan-Martin 2007. Hans Selye was an Austro-Hungarian physiologist and physician Born in Vienna in 1907 who developed a theory to explain general adaptation syndrome GAS.
GAS is the three-stage process that describes the bodys response to stress. Selye was born in Vienna Austria-Hungary on January 26 1907 and grew up in Komárom Hungary. But what do the different stages involve and what examples are there of GAS in action.
These included physical chemical agents and emotional factors. Hans Selye Selye János in Hungarian was born in Komarno Slovakia at that time Komárom Hungary in 1907. Known as the Father of Stress Hans Selye pioneered and.
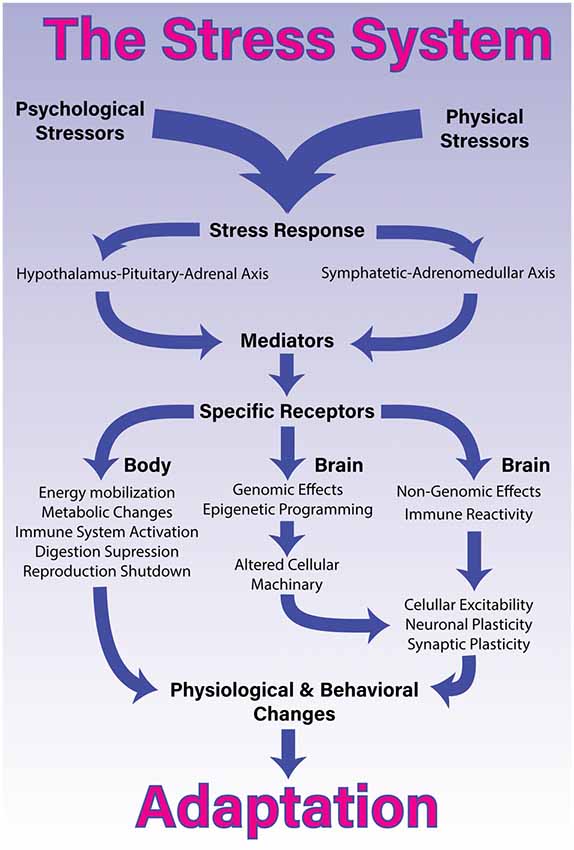
He wrote over 1700 scholarly papers and 39 books about stress. Selye defined stress as a general stereotypical response involving activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal HPA axis and the autonomic nervous system ANS. Selye termed this collection of symptoms as the general adaptation syndrome.
He earned worldwide acclaim for his extraordinary contributions and he was named the Einstein of medicine. But even if you know the physical effects of stress you may be unaware of the different stages of stress known as general adaptation syndrome GAS. The terms general alarm reaction and general adaptation syndrome were proposed for the description of these two phases of the response.
General adaptation syndrome developed by a Hungarian endocrinologist Hans Selye is a theory used to explain how we respond to stress. When you understand the different stages of. Selye defined stress in 1936 in his first scientific paper.
Definition The general adaptation syndrome GAS is a theory of stress responding proposed by Hans Selye. Endocrinologist and Scientist Hans Selye 1907-1982 introduced the General Adaptation Syndrome GAS theory in 1936.
Selye defined stress in 1936 in his first scientific paper.
Known as the Father of Stress Hans Selye pioneered and. The alarm stage the resistance stage and the exhaustion stage Evan-Martin 2007. He distinguished acute stress from the total response to chronically applied stressors terming the latter condition general adaptation syndrome which is also known in the literature as Selyes Syndrome. Selye termed this collection of symptoms as the general adaptation syndrome. Selyes father was a doctor of Hungarian ethnicity and his mother was Austrian. When you understand the different stages of. The terms general alarm reaction and general adaptation syndrome were proposed for the description of these two phases of the response. Endocrinologist and Scientist Hans Selye 1907-1982 introduced the General Adaptation Syndrome GAS theory in 1936. Selye defined stress as a general stereotypical response involving activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal HPA axis and the autonomic nervous system ANS.
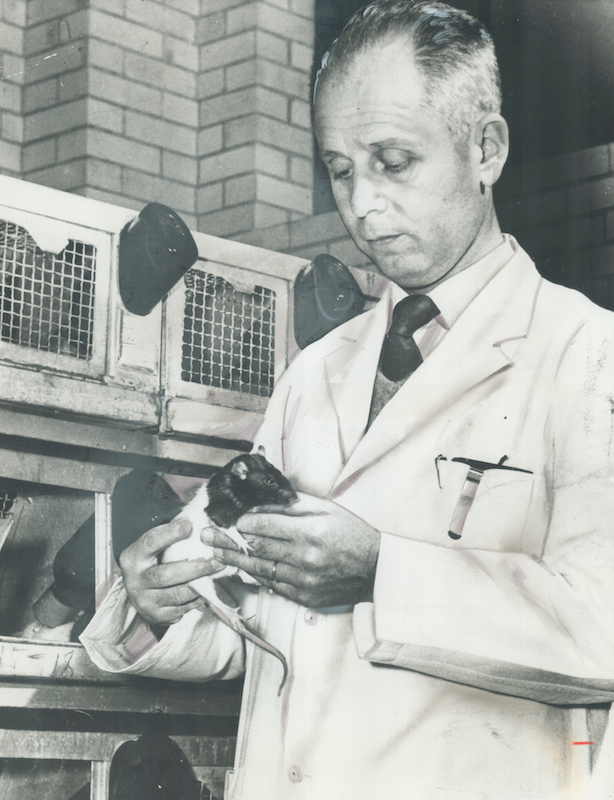
He became a Doctor of Medicine and Chemistry in Prague in 1929 and went on to do pioneering work in stress and endocrinology at Johns Hopkins University McGill University. He wrote over 1700 scholarly papers and 39 books about stress. GAS is the three-stage process that describes the bodys response to stress. General adaptation syndrome is a three-stage response that the body has to stress. These included physical chemical agents and emotional factors. In 1936 Selye defined these series of symptoms in the experiments with the rats as the General Adaptation Syndrome which consists of three stages. Selyes father was a doctor of Hungarian ethnicity and his mother was Austrian.































Post a Comment for "Hans Selye Defined His General Adaptation Syndrome Concept, Which Is Also Known As:"