Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System
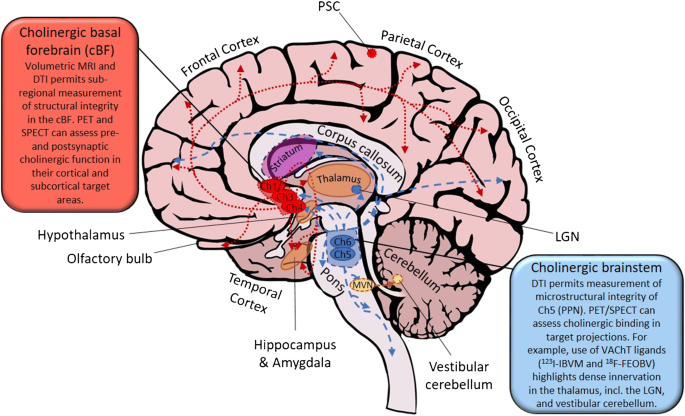
Basal forebrain cholinergic system. The basal forebrain cholinergic neurons BFCN provide the primary source of cholinergic innervation of the human cerebral cortex. Ideally functions would be described for only the cholinergic cells in only this brain area. The basal forebrain BF is located in the rostroventral forebrain and was originally defined by the presence of cholinergic cortically projecting neurons.
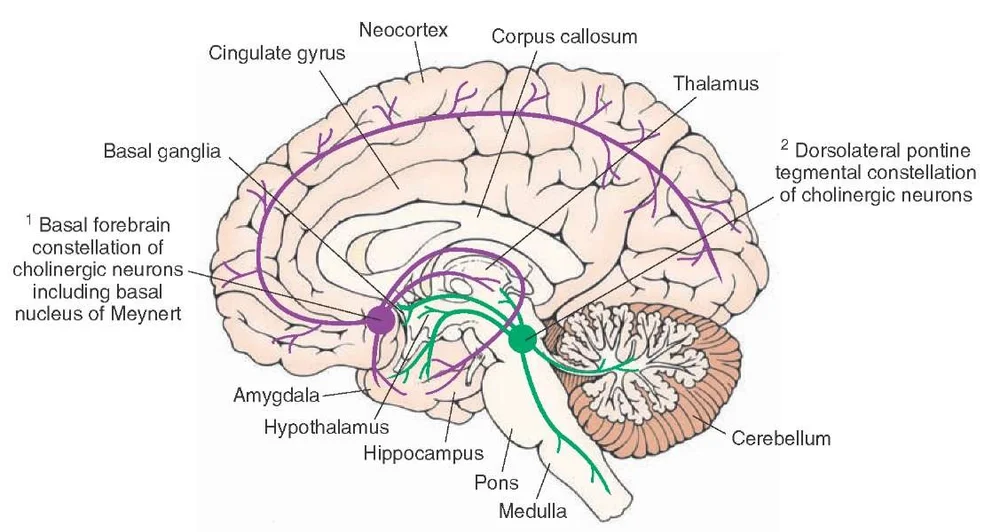
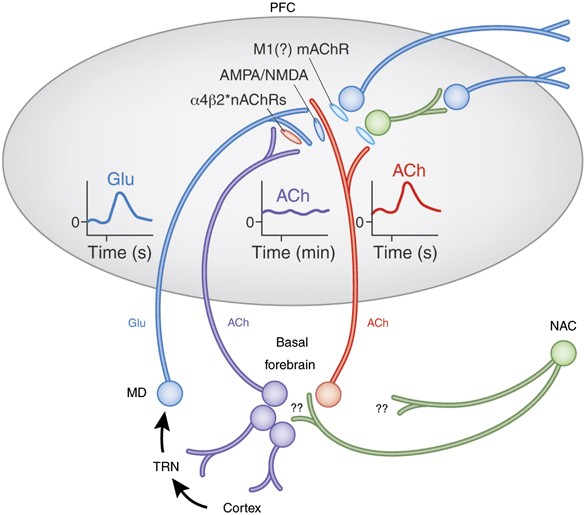
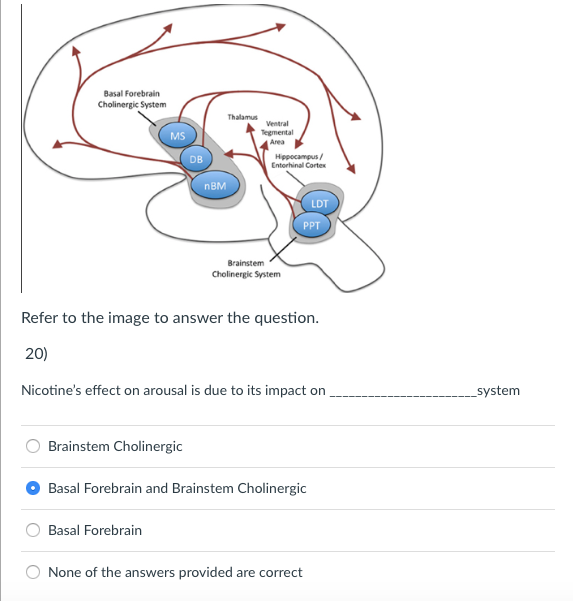
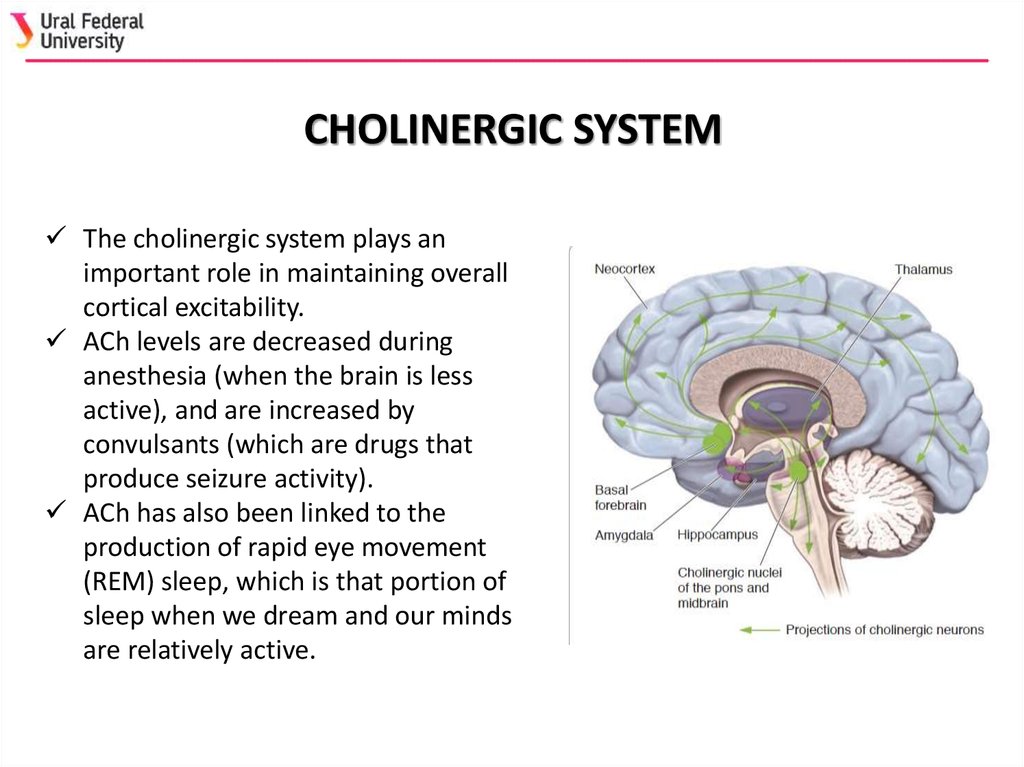
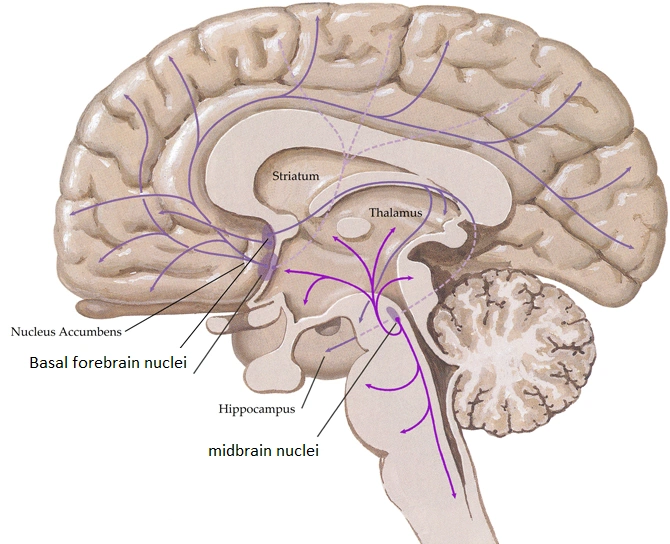
Neuropathological studies suggest that the basal forebrain cholinergic system BFCS is affected in Alzheimers disease AD but there is no in vivo evidence of early damage to this system in subjects at high risk of developing AD. First identified by immunohistochemical staining for AChE the innervation of the cerebral cortex by cholinergic fibers from the basal forebrain was originally proposed by Shute and Lewis 1967 to represent the important relay of the brain reticular activating system to the cerebral cortex within the cholinergic reticular activating system Figure 91. For example inputs from the nucleus accumbens tend to synapse on ventral pallidal cholinergic neurons Zaborszky and Cullinan 1992.
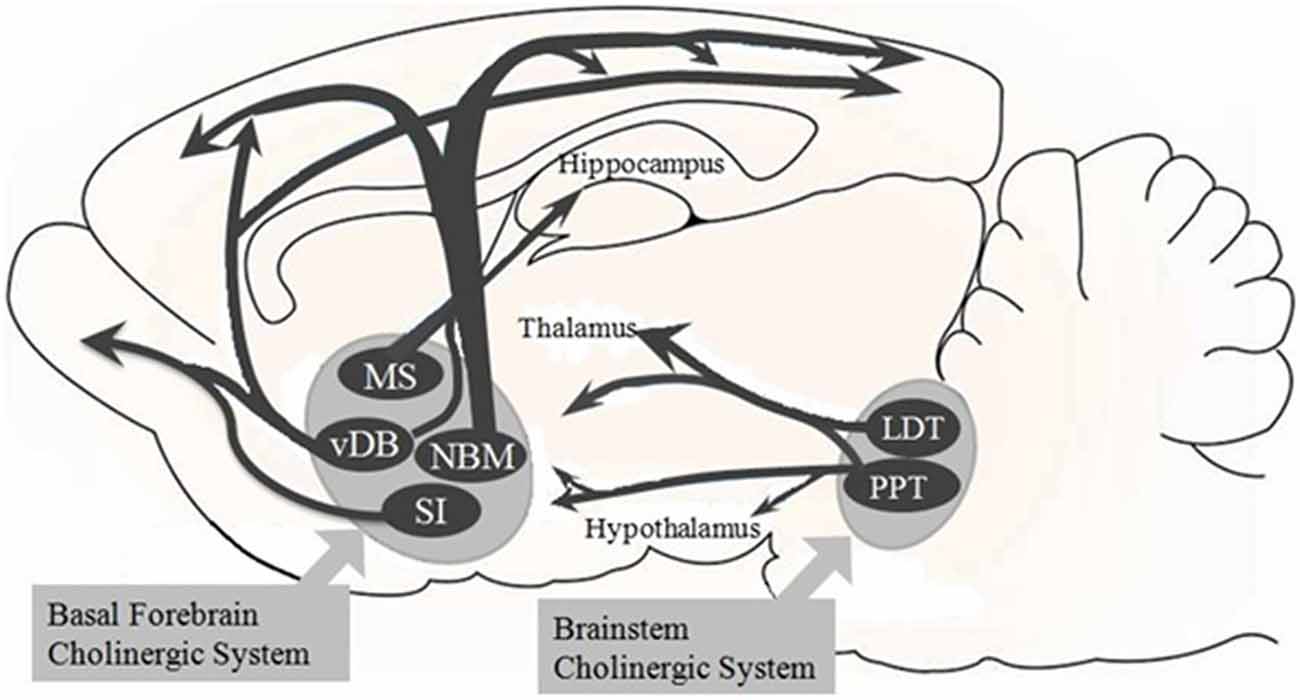
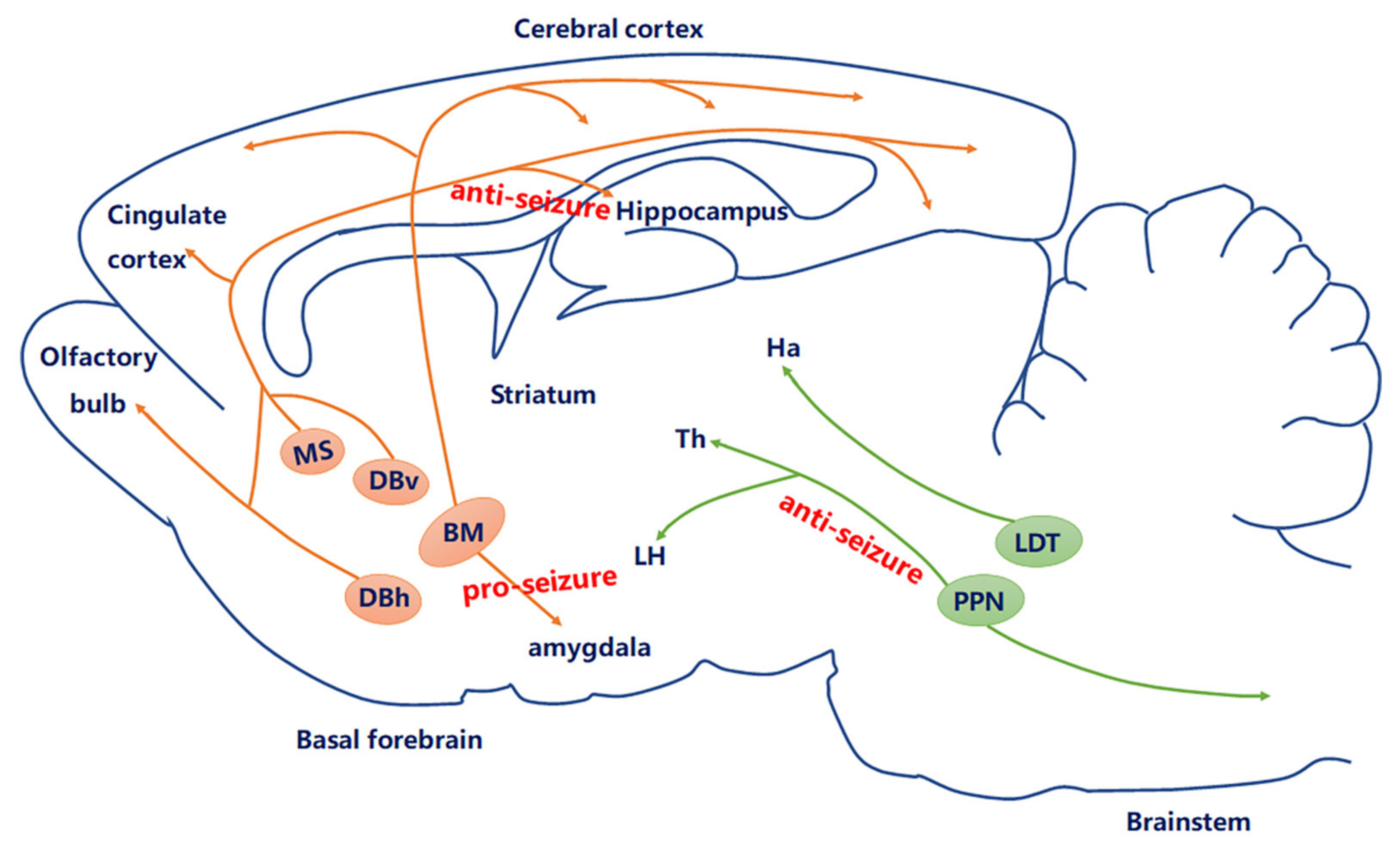
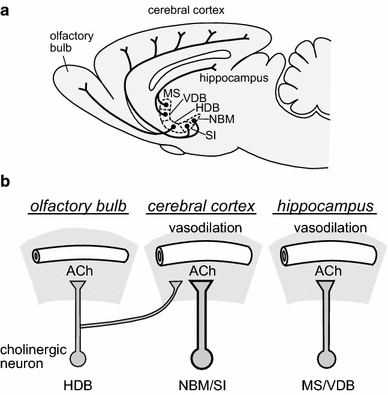
The Cholinergic Hypothesis for AD held that the deficiency of presynaptic neurotransmitter was a. Long-Range Axonal Projections of Cholinergic Neurons in the Basal Forebrain. The BF includes the MS the ventral and horizontal limbs of the diagonal band of Broca VDB and HDB the magnocellular preoptic nucleus MCPO the substantia innominata SI and the ventral pallidum VP.
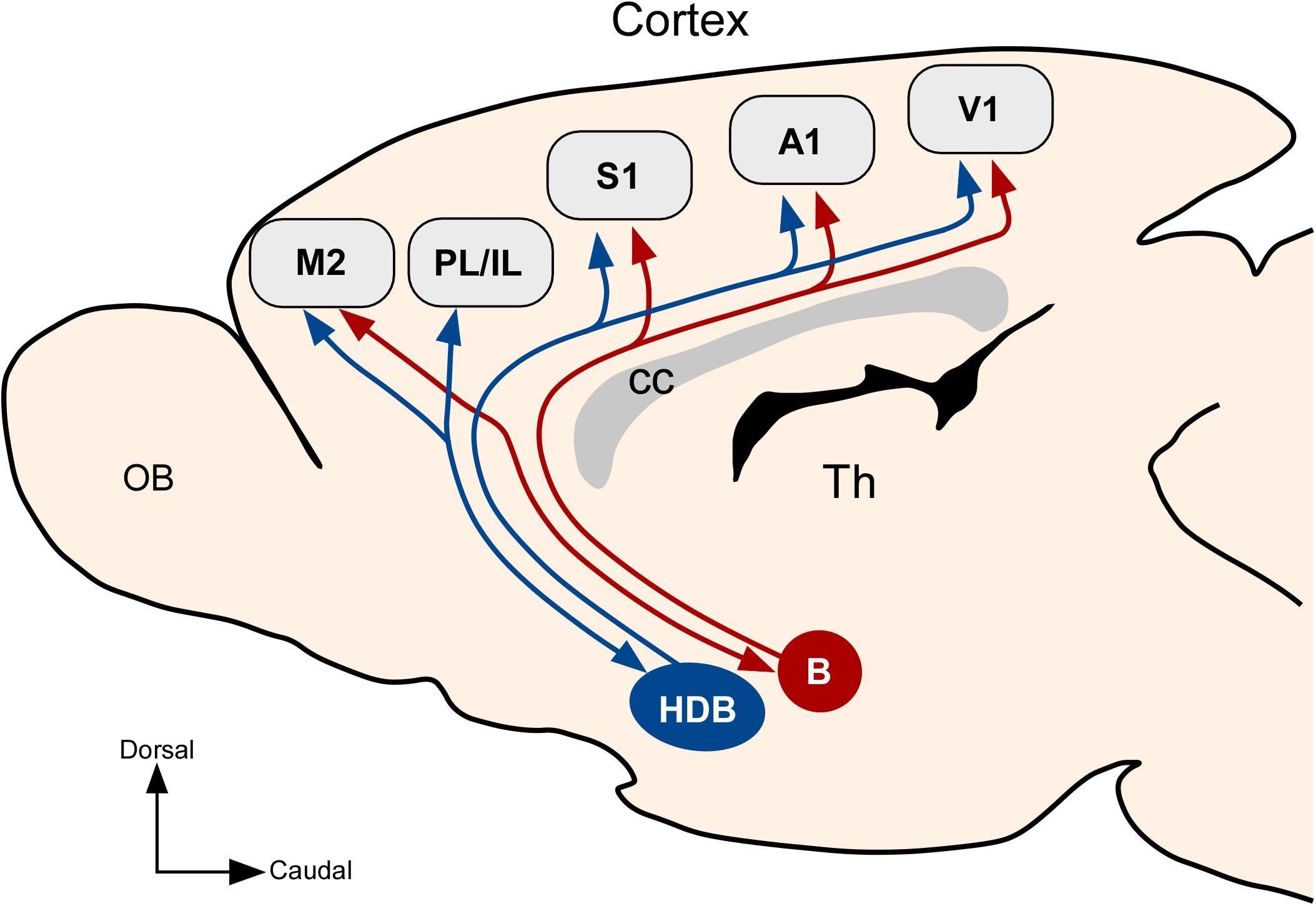
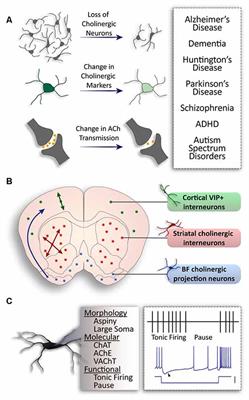
Previous studies have shown that cortical projections of cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain exhibit an anteroposterior preference. The cholinergic system in the brain plays crucial roles in regulating sensory and motor functions as well as cognitive behaviors by modulating neuronal activity. Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimers disease.
It is well established that they are mainly involved in cognitive processes requiring increased levels of arous. Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimers disease. Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons are a cluster of large neurons in the basal forebrain first described by Meynert 1872 and termed the magnocellular basal forebrain system Hedreen et al 1984 or the nucleus basalis of Meynert NbM in primates Koelliker 1896.
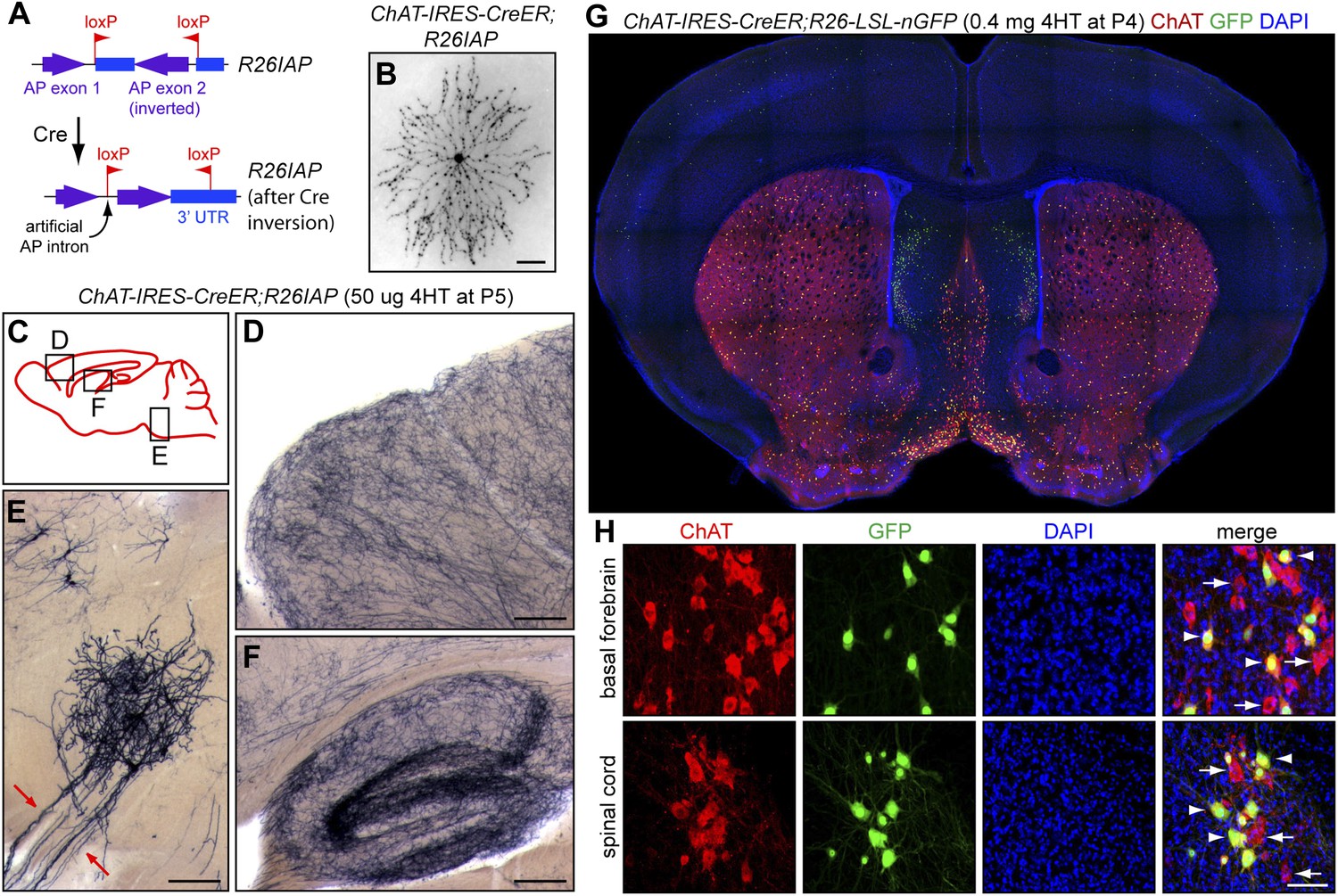
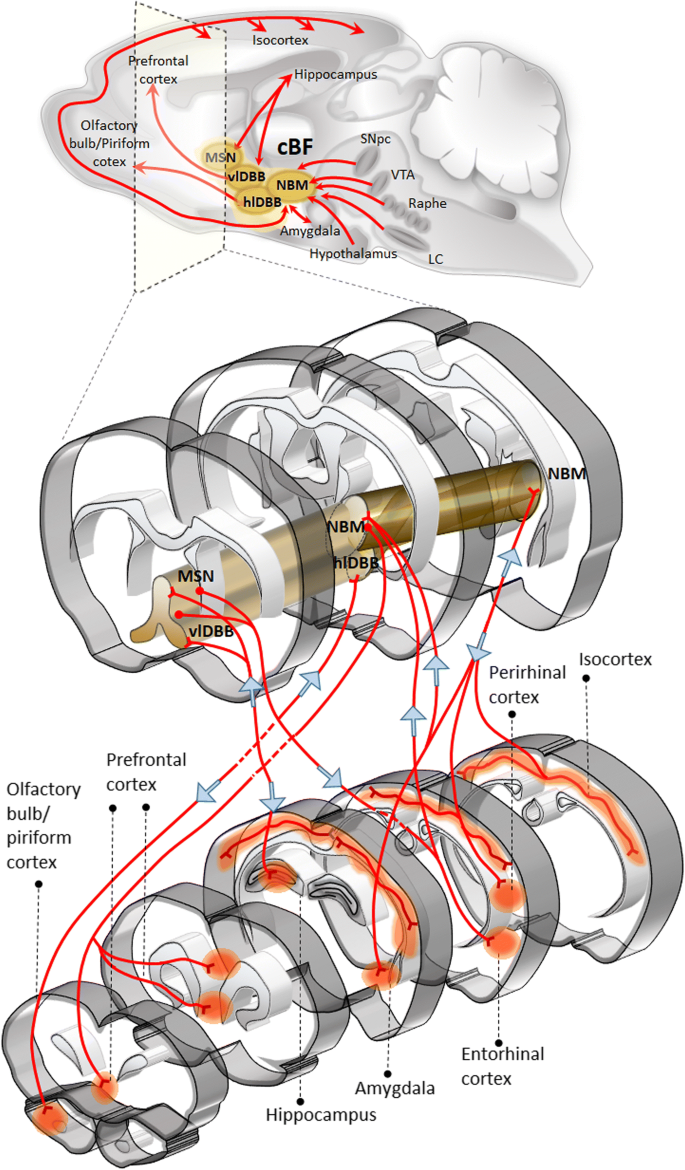
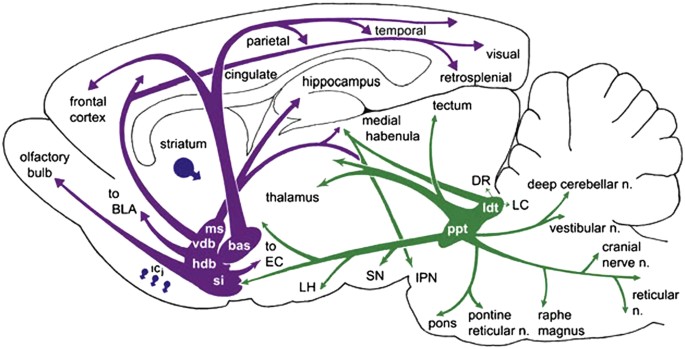
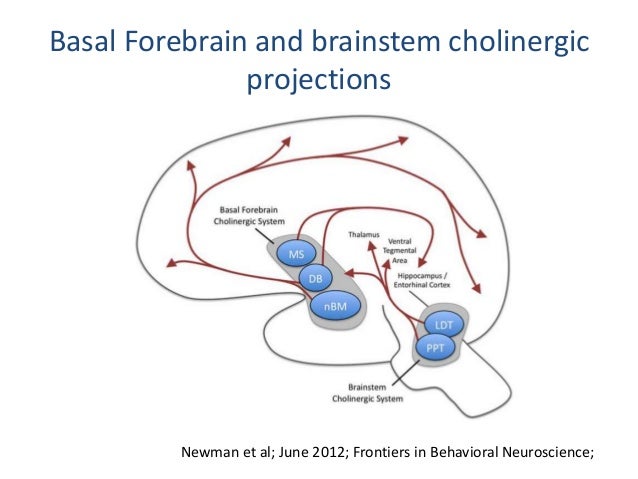
These results revealed a possible model for the cholinergic projectome in the basal forebrain suggesting that a single cholinergic neuron projects to associated functional areas while neighboring neurons can project disparately across the cortical and subcortical areas in contrast to a previous hypothesis. Neurons in the medial septum MS and vertical diagonal band of Broca vDB provide cholinergic projections predominantly to the hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex and neurons in the nucleus basalis magnocellularis NBM provide cholinergic innervations to the entire. A quantitative analysis across subregions of the basal forebrain.
These neurons are differentially vulnerable in various neuropathologic entities that. In the substantia innominate of the basal forebrain it is located the nucleus basalis of Meynert with neurons projecting throughout the cortex and the amygdala.
In the basal fore- brain of mammals cholinergic neurons arelocated in the medial septum Ch1 the vertical Ch2 and horizontal Ch3 limbs of the diagonal band and in the substantia innominatanucleus basalis Ch4 Mesulam et al 1983a.
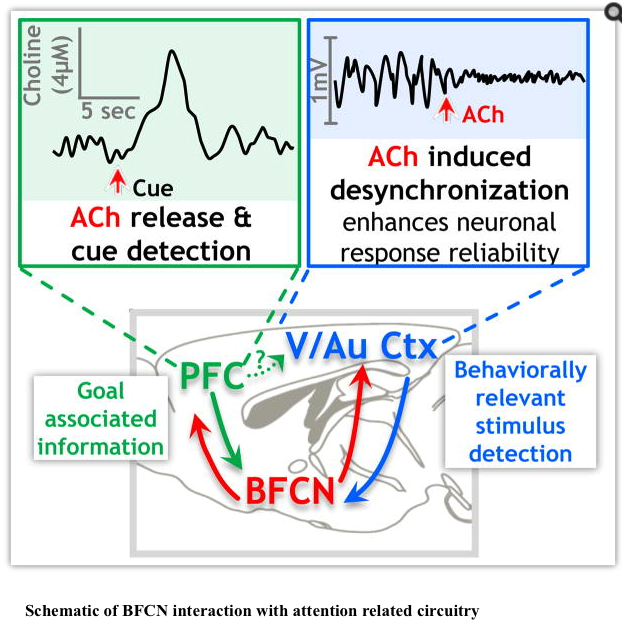
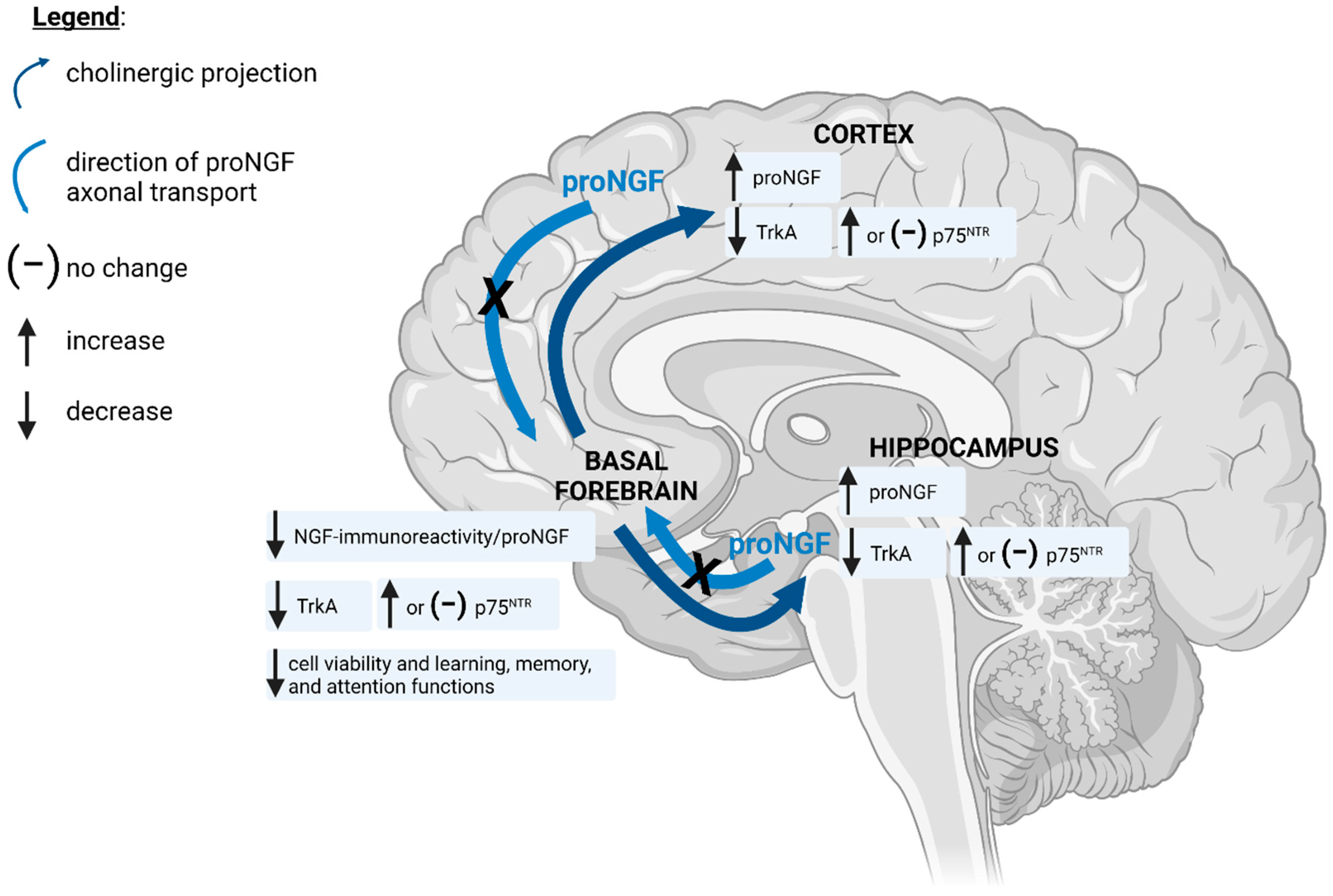
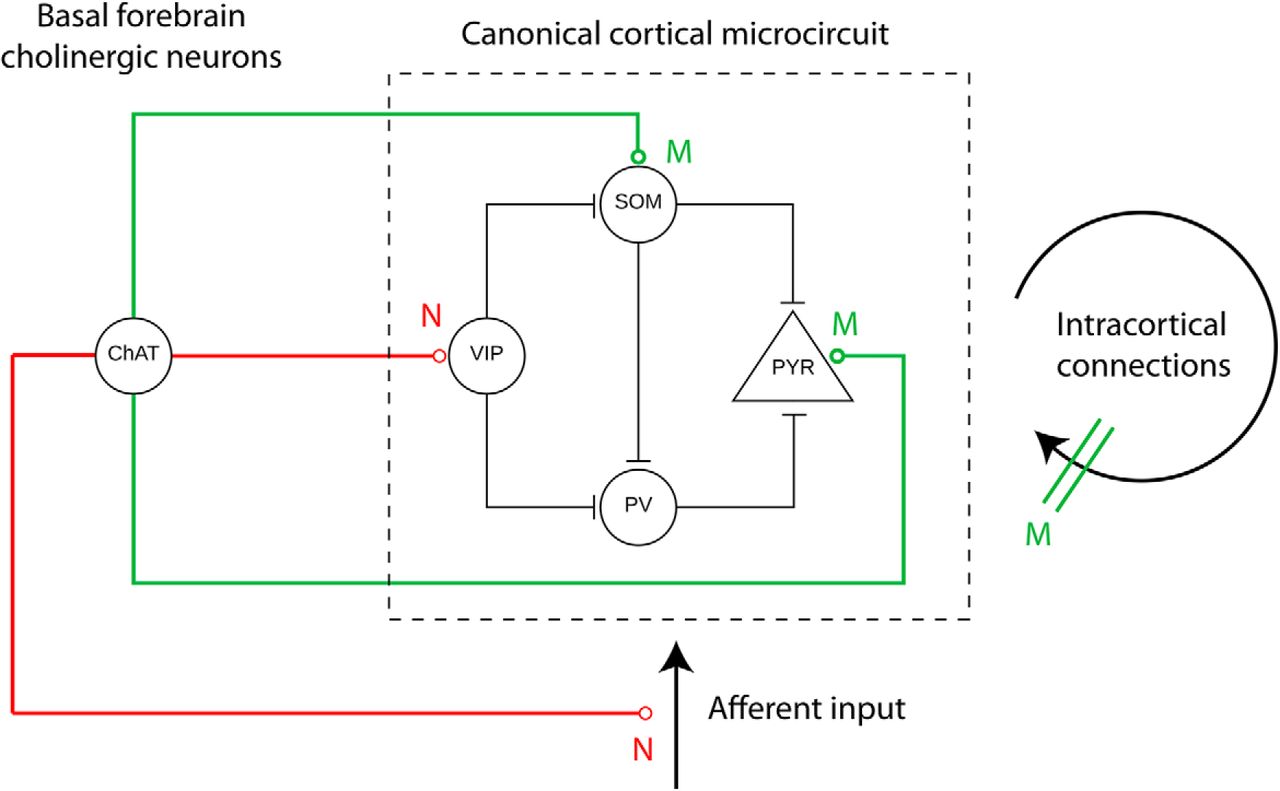
Neuropathological studies suggest that the basal forebrain cholinergic system BFCS is affected in Alzheimers disease AD but there is no in vivo evidence of early damage to this system in subjects at high risk of developing AD. It is well established that they are mainly involved in cognitive processes requiring increased levels of arous. Generation of a whole-brain atlas for the cholinergic system and mesoscopic projectome analysis of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons Xiangning Liab1 Bin Yucd1 Qingtao Sun a Yalun Zhang a Miao Ren Xiaoyan Zhang Anan Liab Jing Yuana Linda Madisene Qingming Luoab Hongkui Zenge Hui Gongab2 and Zilong Qiubc2 aBritton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics Wuhan National. Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System and Memory. Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimers disease. The cholinergic neurons found in the basal forebrain are the most well-known of the CNS cholinergic clusters 109-111. They are involved in the cognitive processes of learning memory and attention. Activation of this system by different afferent inputs is likely to influence how attentional resources are allocated. Previous studies have shown that cortical projections of cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain exhibit an anteroposterior preference.
Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System and Memory. While it has been recognized for some time that the hypothalamus is a signific. Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimers disease. As will be indicated below for technical reasons functional analyses of the BFCS have. In early AD a prominent deficit occurs in cholinergic pathways particularly in the basal forebrain cholinergic system whose afferents project widely to the hippocampus amygdala and neocortical areas. The basal forebrain cholinergic neurons BFCN provide the primary source of cholinergic innervation of the human cerebral cortex. Neurons in the medial septum MS and vertical diagonal band of Broca vDB provide cholinergic projections predominantly to the hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex and neurons in the nucleus basalis magnocellularis NBM provide cholinergic innervations to the entire.


























Post a Comment for "Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System"